France: regions & details
Before the Revolution 1789,
France was divided into provinces.
Each province had its own laws and customs. Languages, cooking, sports, weights and legends were different in each province. To unify the country, the new State reorganised into départements and made laws that applied everywhere.
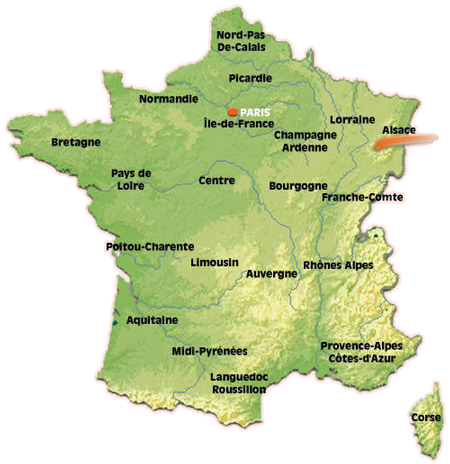
In 1960, the départements were grouped into 27 administrative Regions. Twenty two of these are in Metropolitan France. There are 5 'overseas départements', Guadeloupe, French Guiana, Martinique, Réunion and Mayotte.
The 22 regions are named: Alsace, Aquitaine, Auvergne, Basse-Normandie, Bourgogne, Bretagne, Centre, Champagne-Ardenne, Corse (Corsica), Franche-Comte, Haute-Normandie, Ile-de-France, Languedoc-Roussillon, Limousin, Lorraine, Midi-Pyrenees, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, Pays de la Loire, Picardie, Poitou-Charentes, Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur and Rhone-Alpes.
Learn more about the regions of France --link--
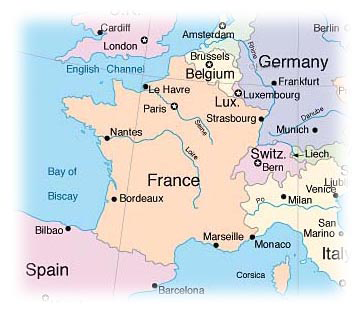
Current day France and
bordering countries
France has 36,500 towns and villages which have the status of a "commune". Whether large or small, all communes have a town hall. At the age of 18 a person may register to vote. The commune is run by the mayor and the town council. These are elected every 6 years. The elections always take place on a Sunday. The town hall has many uses. It is the office where the births, deaths, marriages and divorces are registered (recorded). Also, the French citizen will go to the town hall for such things as identity cards, passports, birth certificates and to get married. The town hall is where a foreigner can get a residence permit.
French Republic: country name, conventional long form
Republique Francaise: country name, local long form
France: country name, conventional and local short form
Government type: republic. Capital: Paris. Independence achieved in 486 (unified by Clovis). National holiday: National Day, Taking of the Bastille, 14 July (1789).
Constitution: 28 September 1958, amended concerning election of president in 1962, amended to comply with provisions of EC Maastricht Treaty in 1992; amended to tighten immigration laws 1993.
Legal system: civil law system with indigenous concepts; review of administrative but not legislative acts.
